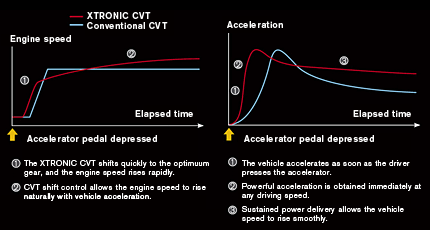
XTRONIC CVT
CVT reduces emissions, provides "driving pleasure"
CVT
(Continuously
Variable
Transmission)
is
a
system
with
seamless,
“stepless”
gear
transmission.
Early
on
Nissan
understood
the
merits
of
CVT,
low-fuel
consumption
and
seamless
acceleration,
developing
and
adopting
the
technology
for
its
vehicles.
Extending
the
attributes
of
the
efficient
CVT
even
further,
XTRONIC
CVT
now
offers
powerful
acceleration
performance
that
is
also
a
pleasure
to
drive.

CVT for 3.5-liter class engine
Technology Functionality
CVT
is
a
“stepless”
transmission
system.
As
opposed
to
MT
(Manual
Transmission)
or
AT
(Automatic
Transmission),
CVT
can
automatically
select
the
most
suitable
transmission
gear
ratio
without
any
steps.
Vehicles
with
CVT
can
run
on
the
most
efficient
(i.e.
with
the
best
fuel
combustion)
engine
rotation
for
regular
velocity.
The
technology
realizes
seamless
performance
without
shift
changes
when
accelerating
and
decelerating.
It
also
expands
the
low-to-high
gear
ratio
range,
with
transmission
gear
ratio
control
matching
the
way
you
drive,
and
delivering
both
excellent
fuel
economy
and
acceleration
performance.
Technology Configuration
CVT adjusts the width of two pulleys and changes the arc radius of the steel belt running between them in order to control the transmission gear ratio.
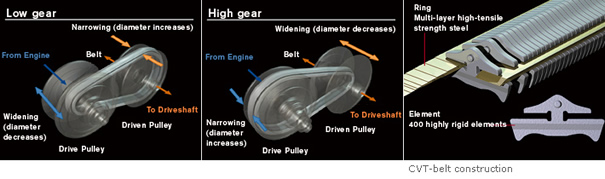
In
the
illustration
above,
the
arc
radius
of
the
belt
for
the
engine
shaft
pulley
gets
narrower.
This
is
ideal
for
driving
at
slow
speeds,
when
gears
on
MT
or
AT
vehicles
are
lower
(for
example,
first
or
second
gear).
On
the
other
hand,
when
in
high
gear,
the
belt
on
the
drive
pulley
gets
wider.
This
is
suitable
for
high-speeds
when
the
gear
is
high,
such
as
in
fifth
or
sixth.
The
steel
belt
is
serving
here
to
bridge
the
two
pulleys
and
change
the
diameter.
If
the
gear
ratio
at
low
gear
is
lowered
even
more,
acceleration
improves.
This
is
the
same
as
how
starting
in
first
gear
has
more
power
than
starting
in
second.
As
well
as
when
moving
off,
vehicle
response
improves
at
lower
speed.
On
the
other
hand,
when
the
gear
ratio
runs
at
a
higher
gear,
the
engine
rotation
decreases
even
at
high
speed,
meaning
there
is
better
fuel
combustion
and
less
noise.
This
is
the
same
logic
as
how
when
driving
on
a
highway
in
fifth
gear
the
engine
rotates
less
than
fourth
gear.
Accordingly,
in
addition
to
the
acceleration,
the
fuel
combustion
and
engine
noise
levels
can
be
improved
by
making
the
low
and
high
gear
ratio
range
(called
transmission
gear
ratio
range)
larger.
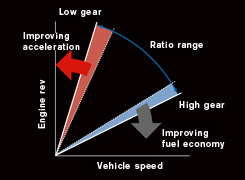
Expanded gear ratio range
XTRONIC
CVT
widened
the
low-to-high
gear
range
of
the
transmission
gear
ratio
through
upgrading
the
pulley
and
steel
belt,
and
the
performance
of
the
ATF
(Automatic
Transmission
Fluid).
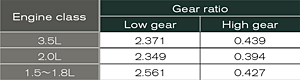
For
1.5-2.0-liter
transmission
it
realizes
top
level
gear
ratio
range.
The
system
is
able
to
reduce
transmission
time
by
around
30%,
realizing
immediate
response
when
you
step
on
the
accelerator
pedal,
and
natural,
powerful
acceleration.
*Gear ratio range: The ratio spread from low to high gear. The low gear ratio divided by the high gear ratio.
With
CVT
the
engine
output
is
transferred
via
the
torque
converter.
The
torque
converter
is
configured
with
an
ATF
and
along
with
working
like
a
clutch,
is
an
important
vehicle
part
for
increasing
torque
and
transferring
powerful
kinetic
force
when
moving
off.
However,
by
going
through
the
ATF
efficiency
decreases,
and
the
fuel
combustion
also
becomes
poorer.
After
take
off
and
when
the
torque
converter's
functions
are
not
needed,
the
most
ideal
situation
is
to
run
the
engine
without
going
via
the
torque
converter
(so-called
“locking
up”).
The
XTRONIC
CVT
was
the
first
such
system
in
the
world
to
apply
a
lockup
damper.
By
expanding
the
lockup
range
to
lower
vehicle
speeds,
the
system
realizes
improved
fuel
combustion.